- Intro
- What Is Collagen?
- Collagen In The Body
- Different Forms Of Collagen
- Types & Benefits
- Sources
- Best Collagen Supplements
There has been a lot of talk about collagen lately… You may have seen an article about it, heard it on the news, or might have even seen a friend or family member scoop some out of a jar, mix it with water, and drink it. If you’re new to the collagen space, you may have a ton of questions brewing about it…
What is collagen? Where is collagen found in our body? How is it distributed? What are collagen peptides? What is hydrolyzed collagen and how is it different than collagen peptides, pure collagen, and gelatin? And what about bone broth? How many different types of collagen are there? Where does collagen come from? Are there any benefits to taking a collagen supplement? What types of collagen supplements are there?
Now, before you get overwhelmed with question overload, just know that by the time you finish this article you will have a better understanding about what collagen is, how it affects your body and your appearance, and why supplementing with collagen is essential to reversing the aging process to help you look and feel years younger…


What Is Collagen?
Scientifically speaking, collagen is a family of proteins made up of long-chains of amino acids that twist into a tightly bound helix conformation. This helix gives collagen the strength it needs to support critical roles and functions in the body such as tissue architecture, tissue durability, and cell-to-cell relationships. (1)
It is the major component that ensures the cohesion, elasticity and regeneration of all connective tissue matrices and can be found in tissues such as skin, blood vessels, bones, tendons, and ligaments. It’s even found in your teeth, cornea, cartilage, digestive tract, and the discs between your vertebrae!
It is made primarily of three amino acids: proline, hydroxyproline, and glycine, but the triple helix itself is made up of more than 1,000 amino acids! Making collagen the most abundant protein in your body. (2)
In layman’s terms, collagen is the glue that holds our bodies together and is responsible for basically everything.
As you approach your 30s your collagen production begins to decline and continues to decline as you age. Leaving your skin, hair, nails, and joints dull, tired, and brittle. 🙈 Additionally, you can experience an increase in wrinkles, fine lines, sagging skin, stretch marks, cellulite, weak and achy joints, poor mobility, and more!
So, needless to say, a healthy supply of collagen is crucial for prolonging a youthful appearance, achieving a healthy weight, and maintaining an optimal quality of life!
How Is Collagen Distributed Throughout Our Body?
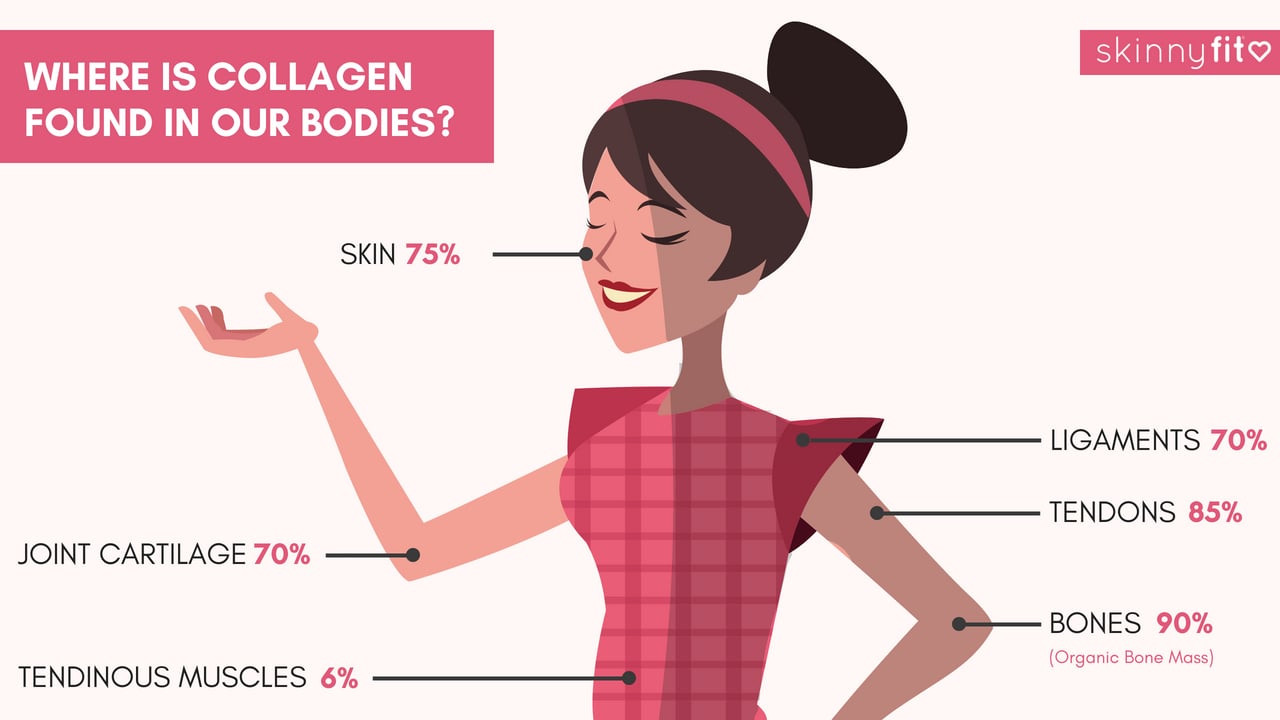
About 30% of your body’s proteins are one type of collagen or another. As I mentioned previously, collagen is found pretty much everywhere. Collagen is distributed throughout your body by weight ratio of dry mass (not including weight from water, blood, etc.) (3)
- Skin 75%
- Joint Cartilage 70%
- Tendinous Muscles 6%
- Ligaments 70%
- Tendons 85%
- Bones 90%
Different Forms Of Collagen
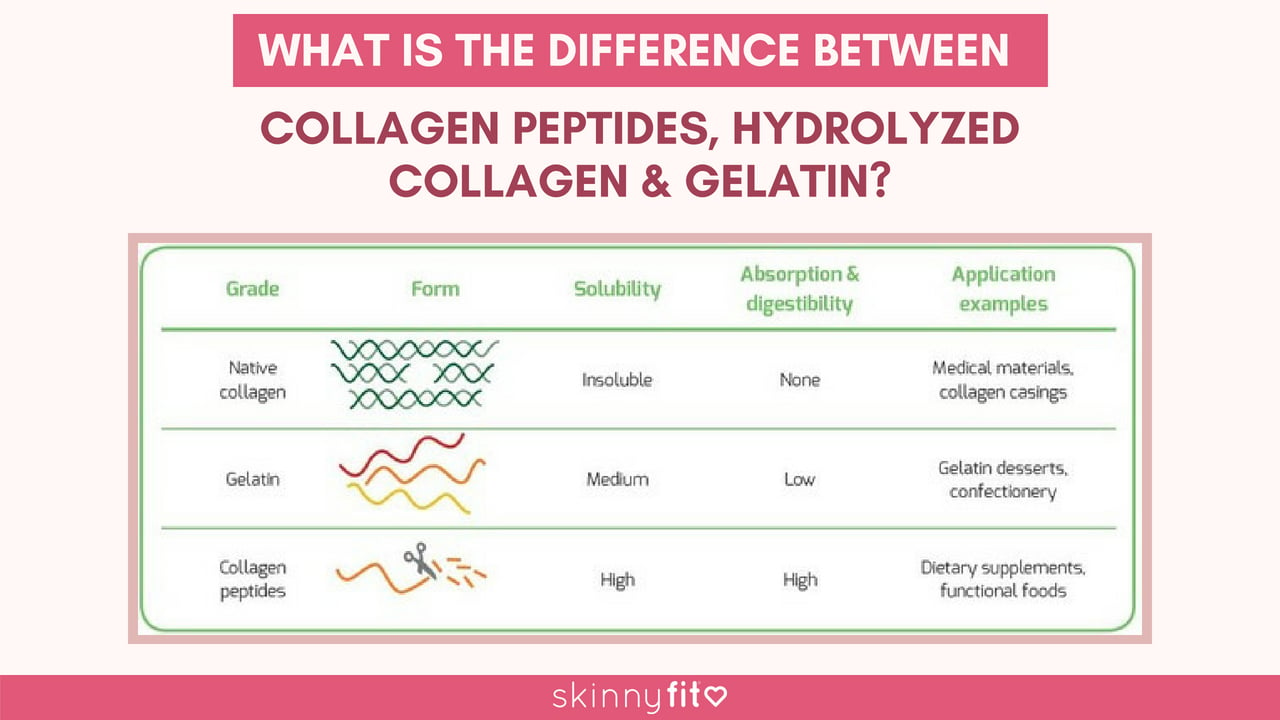
Collagen comes in a variety of forms and understanding the differences will help you determine which is the best type of collagen for you. So allow me to explain the differences between them. What is hydrolyzed collagen and what are collagen peptides? And how are gelatin and bone broth related? If you’re familiar with collagen these are all terms you’ve likely heard before. Sometimes these terms are used interchangeably because they all share the same 18 types of amino acids as well as eight of the nine essential amino acids, so it can be easy to confuse them. However, if you look closely, there are some subtle differences that make each one of these types of collagen unique.
1. Pure collagen
Just to refresh your memory, pure collagen is one long triple helix that contains about 1,000 amino acids.
2. Collagen peptides
Collagen peptides are made after the long chain of pure collagen has been broken down. So a collagen peptide is a section that has broken off from the original collagen helix. Although it is made from pure collagen, it has different properties.
Unlike pure collagen, peptides are much shorter amino acid chains, allowing collagen to be better absorbed into the bloodstream. After absorption, collagen peptides travel throughout the body repairing, rebuilding and providing energy. They’re also shuttled to the different tissues where cells will build the peptides into full-length helices to repair our skin, bones and joints, or the cells can use the amino acids directly for energy.
3. Hydrolyzed collagen
It’s important to understand that hydrolyzed collagen and collagen peptides are the same product but with different names. Full length collagen is broken down into collagen peptides through a process called hydrolysis.
Hydrolysis is the chemical breakdown of the collagen due to a reaction with water. So collagen peptides are frequently referred to as hydrolyzed collagen, collagen peptides, and hydrolyzed collagen peptides.
4. Gelatin
Similar to hydrolyzed collagen, gelatin as gone through a form of hydrolysis. The only difference is that gelatin goes through partial hydrolysis turning it into a gel. Because it has not been fully broken down into peptides, it is not absorbed into the bloodstream as effectively. The partially hydrolyzed chains in gelatin hold onto a lot of water, so supplementing with a gelatin form of collagen can cause bloating and intestinal discomfort.
Additionally, gelatin will only dissolve in hot water, while collagen peptides will dissolve in both hot and cold liquids. Gelatin is difficult to break down during digestion and is too large to cross the intestinal wall, so in its unhydrolyzed, full-length form, collagen is not an effective oral supplement.
5. Bone broth
Bone broth is made by mixing animal bones and connective tissue with water and slowly heating. The collagen in the bones slowly turns into gelatin that dissolves in the water and turns into a broth.
Similar to gelatin, bone broth is not as easily digested into the bloodstream, so it does not have the same healing abilities as collagen peptides. However, adding a scoop of collagen peptides into the broth can increase the benefits, but bone broth alone won’t get the job done.
Types of Collagen & Their Benefits
According to Molecular Cell Biology, there are at least 16 types of collagen, but about 80-90% of the collagen in the body consists of three types [1]. This includes Type I, II, and III. Although it is not as abundant in the body, the presence of Type V is essential for Type I and III to function properly.
Collagen Types I & III
Collagen Type I and Type III are present in scar tissue, tendons, ligaments, muscle, skin, teeth, joints, the organic part of bone, and organ capsules. (4)
Benefits
- Minimizes fine lines and wrinkles
- Improves skin elasticity and smoothness
- Supports bone matrix (36% of bone is made up of these types)
- Corrects weak or damaged nail beds
- Thickens fine hair
- Reduces hair loss
- Improves circulation
- Promotes glycine production which builds lean muscle and helps burn fat during sleep
Collagen Type II
Collagen Type II is found in joints and cartilage. It makes up 50-60% of protein in cartilage and 85-90% of collagen in articular cartilage.
Benefits
- Reduces popping knees
- Supports back, jaw and joints
- Includes glucosamine, chondroitin, and hyaluronic acid
- Improves joint strength and elasticity
- It also makes up the connective tissue of organs and is important for the repair and maintenance of the body. This improves elasticity in tendons and ligaments that decline with age.
Collagen Type V
Type V is essential for formation of Types I and III collagen and supports optimal tissue quality in hair, skin, nails and vital organs, restoring youth from the inside out. It also contributes to the bone matrix; corneal stroma; and interstitial matrix of muscles, liver, lungs and placenta.
Benefits
- Smooths cellulite
- Reduces the visibility of stretch marks
- Supports healthy hair, skin, and nails.
- Improves gut health and digestion
- Soothes IBS, leaky gut, and heartburn
Collagen Type X
Collagen Type X is best known for its healing properties. This type of collagen supports bone formation in cartilage which makes it helpful to prevent normal wear and tear in joints and keeps your body performing at optimal, youthful levels. It is a reliable marker for new bone formation in articular cartilage. (5)
Benefits
- Accelerates healing in muscles, connective tissue, and bone fractures
- Regenerates the strength and flexibility in torn muscles, joints, and ligaments
- Aids in recovery after exercise

Collagen Sources
Now that you have a better idea about what collagen is and understand the difference between the different forms of collagen, the next thing you need to know is where these forms of collagen are sourced from. This is an important detail because where it is sourced plays a vital role in what type of collagen you get, and this directly affects the benefits. There are three different sources of collagen that are used in collagen supplements, beauty products, etc. These animal sources include: marine/piscine (fish), bovine (beef), and fowl (chicken). (7)
1. Piscine/marine (fish)
Collagen that comes from fish is considered to be a superior form of collagen because it raises overall body collagen (Type I), improving skin, hair, nail, and bone quality. Piscine collagen is extremely popular in the beauty industry because it increases skin benefits that provide a glowing, youthful complexion. This is one of the a highest quality collagen sources on the market.
2. Bovine (cow)
Collagen that comes from cows provides a healthy dose of Types I and Type III collagen. It is rich in glycine which is necessary to build healthy DNA and RNA strands and also forms creatine (the compound responsible for protein metabolism).
Beef collagen is the most popular form of collagen supplementation on the market and helps repair connective tissues like joint cartilage, bone matter, and other tendons and ligaments. Additionally, there are some added benefits such as: protein sparing, improves sleep quality, accelerates wound healing, and improves gut health. (6)
3. Fowl (chicken)
This type of collagen sources are particularly effective for supporting cartilage in the body. Type II collagen supplements usually derived from chicken. Although they do help support Type II collagen, they are not as effective as collagen that is sourced from fish.
4. Chicken eggshell membrane
Eggshell membrane is a powerful source of collagen, but surprisingly, not many collagen companies include it in their formula. This type of collagen is responsible for the benefits associated with collagen Types I, II, V, and X!

The Best Collagen Supplements
If you’re curious about what types of collagen supplements are the most effective, I’ve got you covered! Many collagen supplements on the market will contain only one or two types of collagen. This is typically done because it targets a very specific benefit. One of the major downsides to this is that these supplements only offer benefits from one source.
For example, bovine collagen, the most common form of collagen, only increases the benefits for Type I and III collagen, and completely neglects the other three important types of collagen. This means less benefits for the consumer. When selecting a collagen supplement, it’s best to find a product that contains all five collagen types to ensure optimal results.
SkinnyFit Super Youth is a multi-collagen peptide supplement specifically formulated to include all five types of hydrolyzed collagen peptides (Type I, II, III, V, and X) that stem from all three sources (Piscine [wild-caught, pacific snapper], Bovine [grass-fed, pasture-raised cows], and Fowl [cage-free chickens]) to fight all side effects of aging! This high-quality collagen blend has the most diverse collagen ingredients to help you look and feel years younger.
Benefits Of Super Youth Collagen
In addition to its premium ingredients, one of the many reasons why Super Youth is the most desirable collagen supplement on the market is because of how easy it is to incorporate into your daily routine. It comes in a variety of delicious flavors like tropical punch, peach mango, and chocolate cake which can be easily added to water! However, the most versatile type of Super Youth is the unflavored collagen. It’s completely flavorless and odorless and can easily be mixed with any food, or hot or cold beverage. It is also gluten-free, non-GMO, contains 7g of protein and is only 30 calories per serving!
By taking just ONE scoop of Super Youth per day, you can:
- Restore skin’s natural glow
- Increase skin’s hydration and elasticity
- Smooth cellulite and stretch marks
- Reduce wrinkles & even skin tone
- Achieve fuller, healthier hair
- Grow stronger, longer nails
- Brighten teeth and gums
- Support healthy muscles
- Strengthen joints and bones
- Improve gut health and digestion
- Boost fat loss
The Bottom Line On Collagen
There’s no denying that collagen has a significant impact on your health and appearance when taken regularly. There are a variety of different types of collagen, sources of collagen, forms of collagen, and each have their own benefits. When selecting a collagen to take on a daily basis, it’s best to go with a collagen powder that is hydrolyzed and contains all five of the collagen types needed to see visible results. Similarly, you’ll want a collagen peptide that includes all four sources of collagen.
Mentioned In This Post
SkinnyFit Unflavored Collagen
Look and feel younger with Super Youth Multi-Collagen Peptides! This versatile collagen powder includes 5 collagen types from 4 natural sources to restore youthfulness from the inside out.
